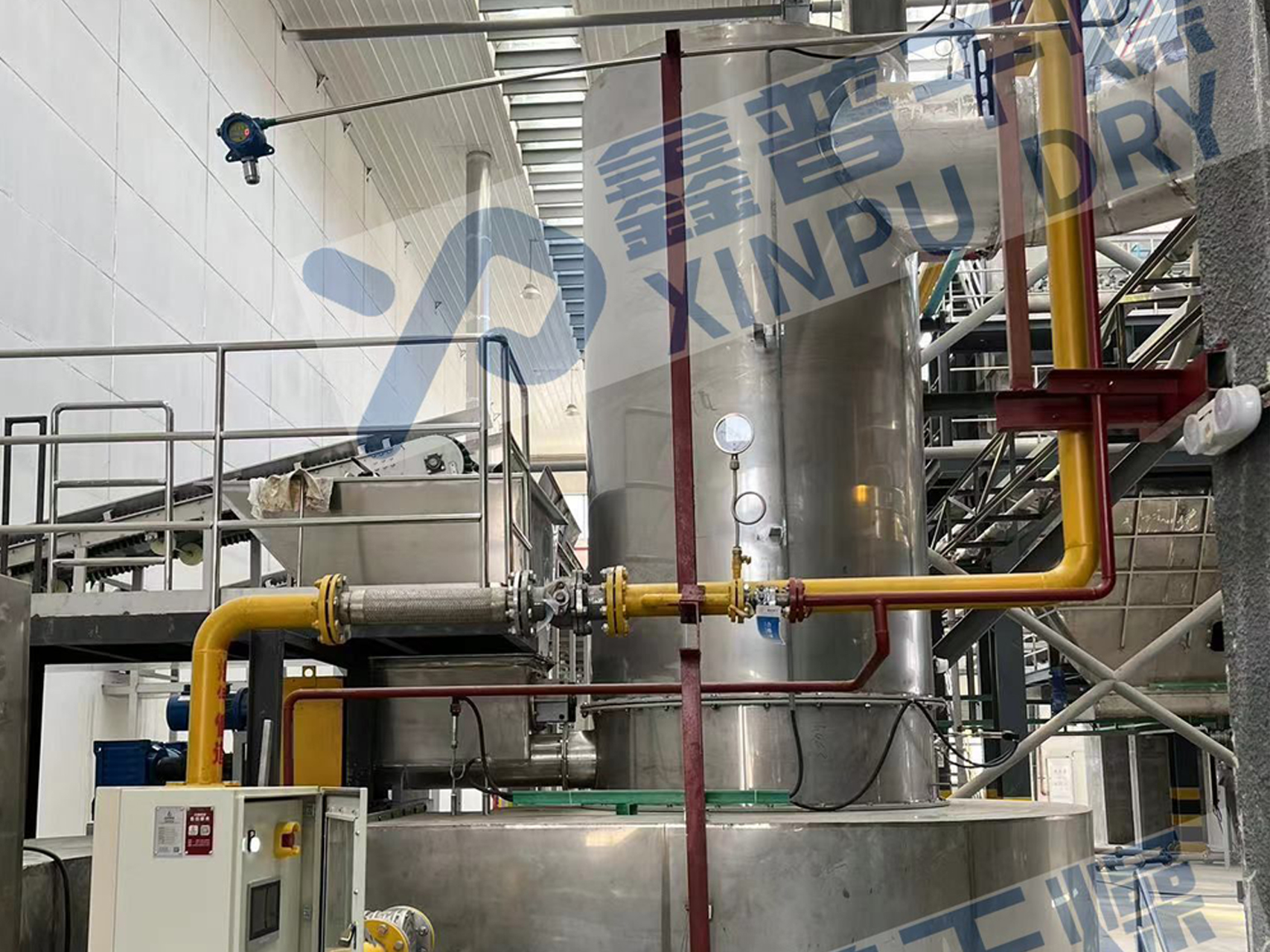
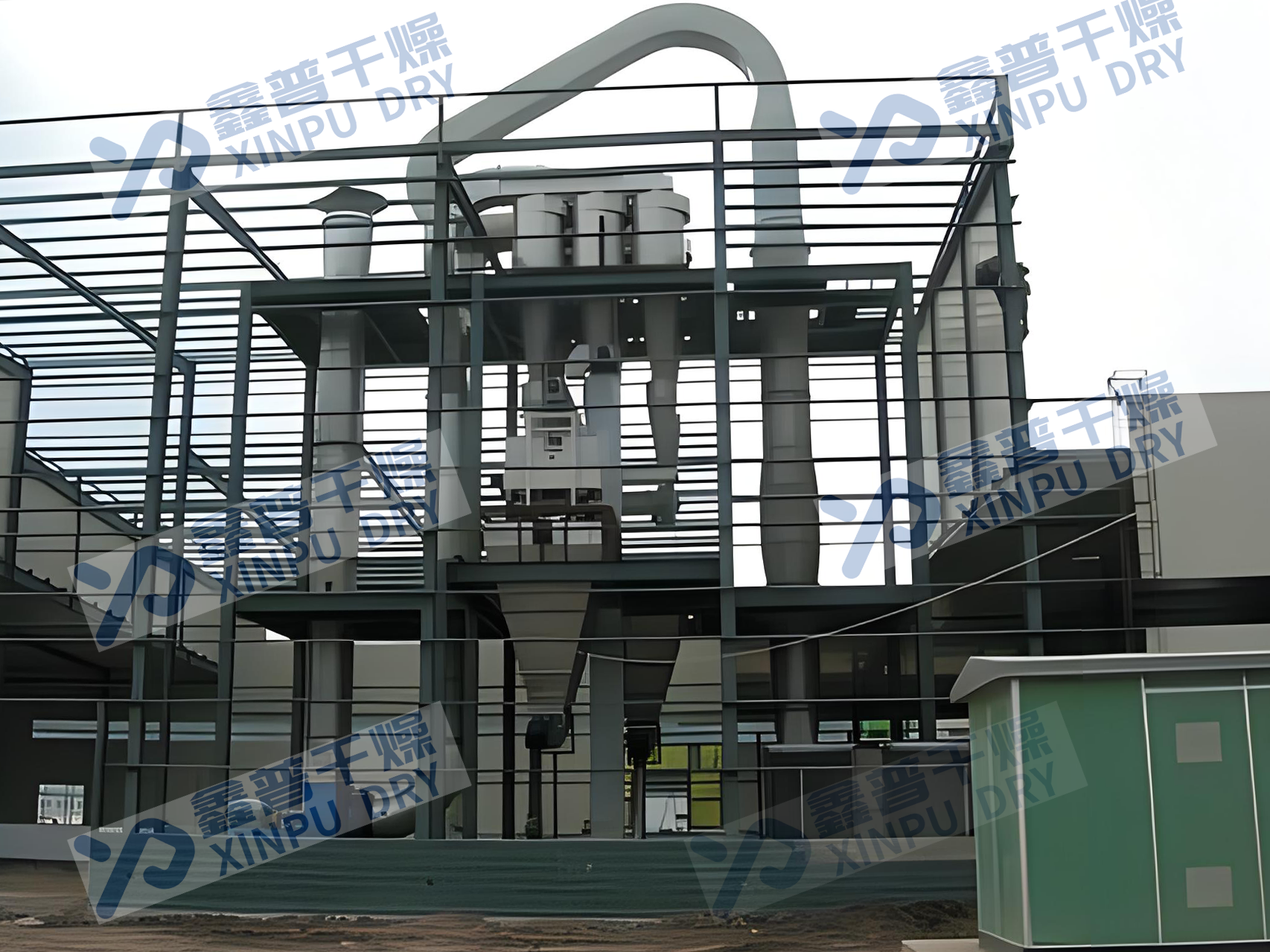
Principle of operation
After the wet material is put in from one end of the dryer, the material is evenly distributed and dispersed in the dryer under the turning of the evenly distributed copying plates in the inner cylinder, and fully contacts with the hot air in parallel flow (countercurrent), which speeds up the heat and mass transfer in drying. In the drying process, under the action of the cylinder with inclination and hot air flow, the residence time of the dried material in the cylinder can be properly controlled by the rotation speed of the cylinder, and finally the finished product is discharged from the discharge port. The dried wet wet tail gas is collected by cyclone separator and bag dust collector, and then exhausted by induced draft fan.
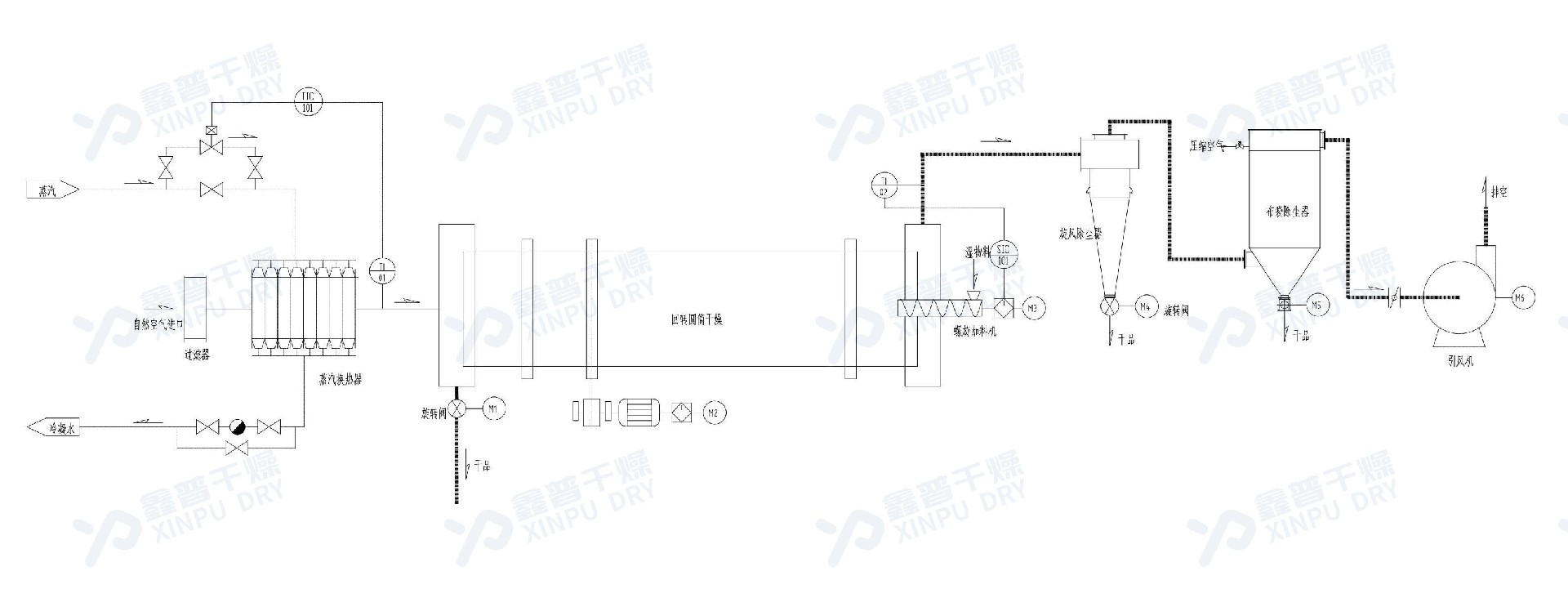
Process flow diagram
Performance characteristics
◎ Rotary dryer has a high degree of mechanization and a large production capacity.
◎ The resistance of fluid passing through the cylinder is small, and the function consumption is low.
◎ Strong adaptability to material characteristics.
◎ Stable operation, low operating cost and good product drying uniformity.
Applied range
◎ Large particles in chemical, mining and metallurgical industries are drier than important materials, such as mines, blast furnace slag, coal, metal powder, phosphate fertilizer and ammonium sulfate.
◎ Drying powder and granular materials with special requirements, such as HP foaming agent, distiller's grains residue, light calcium carbonate, activated clay, magnetic powder, graphite and dregs.
◎ Materials requiring low temperature drying and continuous drying in large quantities.
Technical specifications
Model | Direct heating downstream flow | Direct heating downstream flow | Direct heating countercurrent type | Direct heating countercurrent type | Compound heating | Compound heating |
Material type | Ore | HP foaming agent | Blast furnace slag | Ammonium sulfate | Phosphate fertilizer | Coal |
Handling capacity(kg/h) | 1000 | 466 | 15000 | 20000 | 12000 | 5000 |
Water yield(%) | 30 | 13 | 6 | 1.5 | 5 | 6.5 |
Final water content(%) | 15 | 0.3 | 1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
Average grain diameter(mm) | 6.5 | 0.05 | 4.7 | 0.5-1.7 | 0.5 | 5 |
Material stacking severity(kg/m3) | 770 | 800 | 1890 | 1100 | 1500 | 750 |
Hot air volume(kg/h) | 3900 | 5400 | 10750 | 9800 | 6500 | 16000 |
Inlet gas temperature(℃) | 600 | 165 | 500 | 180 | 650 | 570 |
Material outlet temperature(℃) | 42 | 100 | 70 | 80 | 75 | |
Mode of heating | Coal gas | Steam electric heating | Heavy oil | Coal-fired hot blast stove | Heavy oil | Heavy oil |
| Loading coefficient | 6.3 | 7 | 7.5 | 7.8 | 18 | |
| Rotation speed(rpm) | 4 | 4 | 3.5 | 3 | 4 | 2 |
| Inclination | 0.04 | 0.005 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.043 |
| Number of copying boards | 12 | 24 | 12 | 22 | Outside the inner cylinder 8 Outside the inner cylinder 16 | 6 12 |
| Dryer diameter(m) | 2.0 | 1.5 | 2 | 2.3 | Outer cylinder 2 Inner core 0.84 | Outer cylinder 2.4 Inner core 0.95 |
| Dryer length(m) | 20 | 12 | 17 | 15 | 10 | 16 |
| Driving power(kw) | 22 | 7.5 | 15 | 11 | 11 | 15 |








